Currently Empty: ₹0.00
 Current Affairs | Geography
Current Affairs | Geography
Ethiopia’s Hayli Gubbi Volcano Ash Cloud Reaches India
1) What Happened? (Event Overview)
-
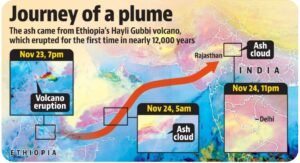
Ethiopia’s Hayli Gubbi volcano erupted after nearly 10,000 years.
-
Ash cloud entered India on Monday evening, first hitting Gujarat, then Rajasthan, NW Maharashtra, Delhi, Haryana, Punjab.
-
Ash plume is moving towards the Himalayas at 100–120 km/hr.
-
Volcano lies in the Afar Rift Valley, a highly active tectonic zone.
2) Ash Cloud Features
-
Ash height: 15,000–25,000 ft (some layers touched 45,000 ft).
-
Contents: Volcanic ash, sulphur dioxide (SO₂), tiny particles of glass and rock.
-
Skies may appear darker, hazier, visibility may dip.
-
Chances of ashfall on plains: Low.
3) Impact on Indian Cities
-
Affected regions: Gujarat, Rajasthan, Delhi-NCR, Haryana, Punjab, NW Maharashtra.
-
Plume already above Delhi and Western UP late Monday night.
-
Expected to influence Himalayan areas and Nepal hills (SO₂ increase).
4) Will AQI Worsen? (Safety Update)
-
NO major impact on India’s ground-level AQI.
-
Reason: Ash is at high altitude (25,000–45,000 ft).
-
Only sky darkening and haziness possible.
-
Some SO₂ may affect Himalayan–Nepal hills & UP Terai region.
5) How Did the Ash Travel?
-
Eruption began: Sunday, 8:30 am GMT (VAAC, Toulouse).
-
Ash rose 14 km high, then drifted over:
Red Sea → Yemen → Oman → Arabian Sea → India → Pakistan.
6) Aviation Impact
-
Airlines issued warnings due to ash in Middle East airspace.
-
DGCA advisory:
-
Avoid ash-affected routes.
-
Adjust flight plans & fuel load.
-
Inspect runways if ash is suspected.
-
-
Flight disruptions: Akasa, IndiGo, KLM cancelled some flights.
-
Mumbai Airport alerted passengers of route impacts.